Introduction
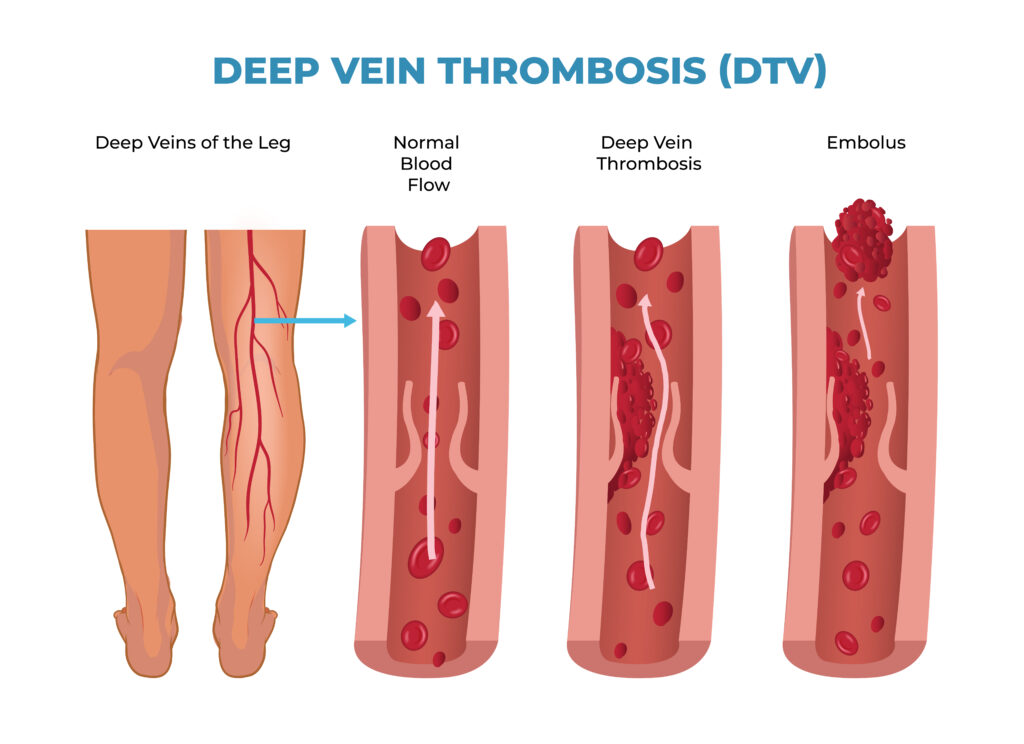
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a condition where a blood clot forms in a deep vein, usually in the leg. This clot can block blood flow, causing pain and swelling. Sometimes, the clot can travel to the lungs and cause a serious problem called a pulmonary embolism. Because DVT can be dangerous, it is important to know the signs, causes, and ways to prevent it. In this overview, you will learn about Deep Vein Thrombosis, its symptoms, risk factors, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention tips.
Symptoms
Often, DVT does not cause any symptoms. However, some people may notice changes in their leg. For example, you might see:
Sometimes, these symptoms can be mild. But if you notice them, you should talk to a doctor right away. Early treatment can help prevent serious problems.
Causes and Risk Factors
Blood clots can form when blood flow slows down or changes. There are many reasons why someone might get Deep Vein Thrombosis. Some common causes and risk factors include:
Because some people have more than one risk factor, it is important to know your own risks. If you have any of these, you should discuss them with your healthcare provider.
Diagnosis
Doctors use several methods to check for Deep Vein Thrombosis. First, they will ask about your symptoms and medical history. Next, they may do a physical exam. If DVT is suspected, your doctor might order tests such as:
Early diagnosis is important. That way, you can start treatment quickly and lower your risk of complications.
Treatment Options
Treating Deep Vein Thrombosis helps prevent the clot from getting bigger or moving to the lungs. Common treatment options include:
Your doctor will choose the best treatment based on your health and the size of the clot. Most people need to take blood thinners for several months.
Prevention Tips
There are many ways to lower your risk of Deep Vein Thrombosis. For example, you can:
If you are at high risk, your doctor may suggest special stockings or medicine to prevent clots.
Lifestyle Guidance for Patients
Living with Deep Vein Thrombosis means making some changes. However, these steps can help you stay healthy:
With the right care, most people recover well and avoid future problems.
When to Seek Medical Help
Sometimes, Deep Vein Thrombosis can lead to a life-threatening problem called a pulmonary embolism. You should get emergency help if you notice:
These signs mean the clot may have moved to your lungs. Quick treatment can save your life. If you have any symptoms of DVT or a pulmonary embolism, call your doctor or emergency services right away.
Conclusion
Deep Vein Thrombosis is a serious but treatable condition. Knowing the symptoms, causes, and ways to prevent it can help you stay safe. If you have concerns or notice any warning signs, consult a healthcare specialist for personalized advice on Deep Vein Thrombosis.