Coronary and Peripheral Angioplasties are minimally invasive procedures designed to open up blocked or narrowed arteries in the heart (coronary arteries) or in other parts of the body (peripheral arteries). These procedures help restore normal blood flow, reducing pain, improving function, and preventing more serious complications like heart attacks or stroke.
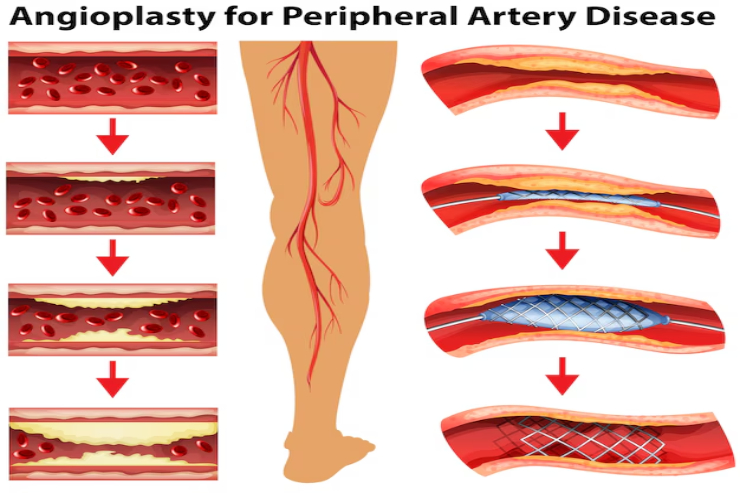
Angioplasty is a procedure where a small balloon is used to widen blocked or narrowed arteries. During the procedure, a thin tube called a catheter is inserted into the affected artery, and a tiny balloon at the tip is inflated to push the plaque (fatty deposits) against the artery walls. This helps to open the artery and restore blood flow. In many cases, a stent (a small metal mesh tube) is placed to keep the artery open and reduce the risk of future blockages.
Coronary Angioplasty is specifically performed on the arteries that supply blood to your heart. If you’ve been diagnosed with coronary artery disease (CAD) or have experienced chest pain (angina) or a heart attack, angioplasty can be life-saving. By reopening the blocked artery, blood flow is restored to the heart, relieving symptoms and reducing the risk of future heart problems.
Peripheral Angioplasty targets blockages in the arteries that supply blood to the limbs, kidneys, or other parts of the body. This is commonly used to treat Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD), where narrowed arteries can cause pain, cramping, and reduced function in the legs or other areas. By widening these arteries, the procedure improves circulation, alleviating symptoms like leg pain and improving mobility.